LED strip lights are known best for their flat structure and modern lighting output. But have you ever thought about how these thin light fixtures work?
LED strip lights have numerous LED chips arranged throughout the circuit board. As electric current passes through the LED chips, they produce energy in the form of light through the electroluminescence process. Much more science is related to the color of the emitted lights. Besides, numerous factors like- voltage, LED chip quality, current flow, etc., affect the final light output.
So, fasten your seatbelt to dive into the world of science to explore how LED strip lights work-
What Is LED Strip Light?
LED strip lights are flexible printed circuit boards populated with light-emitting diodes. They have rope or tape-shaped structures that can be mounted to any area – ceiling, walls, corners, or tight spaces. The most remarkable feature of LED strips is that you can cut them to your required length. Besides, they have advanced features that regular LED lights lack.
The slim-fit design of LED strip lights makes them suitable for interior and exterior lighting. These lights are available in different color variations. You can also have greater control over the lights by integrating them with remote control.
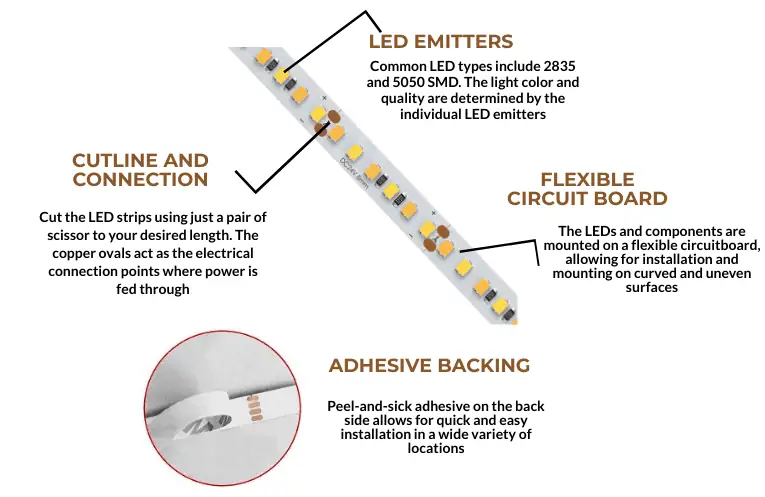
Components Of LED Strip
The essential component of LED strips includes the following-
- LED chips: LED chips are the light-emitting component of LED strips. They are arranged throughout the LED strips. These LED chips emit light when electricity is passed through the strip. The color of the emitted light depends on the color of the LED chip. Single-color LED strips contain only one color chip, whereas RGB LED strips contain red, green, and blue LED chips. The quality of an LED strip greatly depends on its chip. Check this article for the best LED chip manufacturers- Top Famous LED Chip Manufacturers List (2023).
- Circuit board: The LED strip has a printed circuit board that acts as the structure body of the fixture. This defines the rope shape of the LED strip. The LED chips and other components are arranged within this board. To know more about FPCB, check this – Everything You Should Know About FPCB.
- Driver: low or constant-voltage LED strips require a driver to regulate the current and voltage supply. It ensures appropriate power is supplied to the LED strips for optimal performance. However, high-voltage LED strips don’t need a driver. To know more about LED driver, check this A Complete Guide to LED Drivers.
- Controller: A controller is used to adjust the brightness and color of the LED strip. They can be of different types: IR controller, Bluetooth/Wi-Fi controller, DMX LED controller, Zigbee controller, etc. To know more about LED strip controllers, check this- LED Controller: A Comprehensive Guide.
- Resistors: Resistors are integrated into the circuit of LED strips to limit the current flow. It prevents the strips from overflowing current due to overvoltage, which can damage the fixture.
- Cut points and connectors: The copper dotted mark (usually three dots) present in the PCB of LED strips are marked as cut points and connectors. These dots indicate the cutting mark where you can safely cut the strip without harming its circuit. Again, you can connect the cut pieces or another strip to the dots if you wish. To know more about cut points and connectors, check this- Can You Cut LED Strip Lights and How To Connect: Full Guide.
- Encapsulation: The encapsulation of the LED strip protects the LED chips and other components on the circuit board from ingress. This is usually made of an epoxy or silicone layer that prevents direct contact of the LEDs with water, moisture, or dust.
- Heat Sink: Heat sinks are integrated within the fixtures to prevent the LED strips from overheating. However, LED strips don’t easily get overheated, but high-voltage strips can face these issues. In this case, the heat sink despairs heat away from the light source, keeping it cool. To know more, check this article- LED Heat Sink: What Is It and Why It’s Important?
- Adhesive Backing: The LED strips are easy to mount with adhesive backing. You simply need to remove the tape and press it to the installation surface; that is it! Check this to get a total guideline on LED strip adhesive- How to Choose The Right Adhesive Tapes For LED Strip.
Types Of LED Strips Based On Working Principle
Based on the working principle of LED strips, they can be divided into two categories- analog and digital. These are discussed below-
Analog LED Strip

Analog LED strips are known as standard or non-addressable LED strips. They come in single-color or full-color spectrum (RGB). You can cut these LED strips to your required length. Usually, there are dots or scissor markings after every 5 cm or 10 cm to indicate the cutting points. (It may vary from brand to brand; some brands also offer customization options on cutting length). Analog LED strips are cheaper than digital ones. They come in reels, usually 5 meters/ reel. You will also find options in choosing the LED density or the number of LEDs per meter. Example of analog LED Strip- Single Color LED Strip. The basic features of an analog LED strip are as follows-
- Non-addressable
- Do not have any IC chips
- Cuttable

- Working Principle
LED strips are divided into small segments; every cut mark length’s beginning and ending point is termed a segment. Usually, each segment contains three LEDs or six LEDs. Each of these LEDs is connected in a series circuit. This adds up the operating voltage of each chip and provides a higher voltage to the LED strip. Then, the LED strip connects all the segments in parallel series. This allows constant voltage distribution. That is why the current consumption increases as you increase the length of the LED strip.
- Control Method
Analog LED strips use a basic single-channel control method that includes adjustment of voltage levels and Pulse Width Modulation (PWM). As the voltage increases, the light looks brighter, and with its decrement, the glow dims. On the other hand, the PWM operates by abruptly turning on and off the LEDs at a predetermined frequency. The perceived brightness is determined by dividing the duty cycle (or the time LEDs are on) by the entire time. As a result, brighter lighting is produced by greater duty cycles, whereas dimmer lighting is produced by lower duty cycles. You can control these LED strip lights using dimmers or remote controls.
- Color Control
Analog LED strips can be either single color or RGB. The single-color LED strips come in a particular color like- white, warm white, red, green, etc. Analog LED strips use the PWM method to control the color of these strips. But for RGB LED strips, light color is controlled by mixing different light colors. For instance, if you want to bring yellow color light, it mixes yellow and red light to bring yellow.
- Applications
Analog LED strips are ideal for spaces with sufficient synchronized color changes or single-color lighting. For example, you can use them for accent lighting, task lighting, and other decorative lighting in your house or office.
Digital LED strip
You might have seen the rainbow-like color flow in a single LED strip; these are digital LED strips. This LED strip contains a driver chip and IC chip that allows individual control over each segment of the LED strip. For this reason, they are called addressable LED strips. Besides the magical lighting appearance, digital LED strips are also referred to as magic LED strips or dream color LED strips. Digital LED strips are divided into two main categories: DMX512 digital LED strips and SPI digital LED strips. The basic features of digital LED strips are-
- Addressable
- Have driver chip and IC chip
- Cuttable

- Working Principle
Each LED on the digital LED strip has its microcontroller, which allows for independent control (IC) of every LED. These microcontrollers are connected in series along the strip and communicate using a digital data protocol. A central controller sends control signals to the LED strip, instructing for the color and brightness of each LED. As the control signals travel down the strip, each microcontroller reads its portion of the data and processes the instructions. The microcontroller then adjusts the intensity of its respective LED’s red, green, and blue components, resulting in the desired color and brightness. This process repeats for each LED along the strip. Thus, it allows for dynamic lighting effects, animations, and patterns, as each LED can display different colors and brightness levels independently. To know more, check this article- The Ultimate Guide To Addressable LED Strip.
- Control Method
Digital LED strips use an individual control method. That is, each of the segments can be controlled individually. A central controller, like an Arduino or Raspberry Pi, sends commands to each LED segment. Following the command, the LED changes its colors accordingly. Thus, it gives precise and customized control over the strip, making them ideal for applications that require dynamic lighting displays.
- Color Control
You can have extensive color control over the digital LED strip. It allows you to select the color output of every segment of the strips. Thus, you can create multiple colors in a single LED strip at a time.
- Applications
Digital LED strips are excellent for events like- concerts, parties, festivals, etc. You can also use these lights for decorating commercial spaces like- bars, motels, pubs, gyms, KTV, etc.
Analog LED Strip Vs. Digital LED Strip
| Criteria | Analog LED Strip | Digital LED Strip |
| Addressable | No | Yes |
| IC chip | Not present | Present |
| Control Method | Single-channel control | Individual control |
| Color Control | Limited: one color for the whole LED strip at a time | Dynamic: different colors for every section of LEDs |
| Cost | Standard | Expensive |

Working Mechanism Of LED Strip Lights
The working mechanism of LED strip light is conducted through the electroluminescence process. The LEDs on the LED strip are composed of semiconductor materials. When electricity is passed through these materials, they emit light. This process is known as electroluminescence, which is how LED strips produce light. The working mechanism is discussed below in detail-
Light Emitting Mechanism
The LED chip that remains arranged throughout the LED strips is made of two layers of semiconductor material. These are – p-type semiconductors and n-type semiconductors. The P-type semiconductor has positively changed holes. In contrast, the n-type semiconductor has excess electrons and is negatively charged. The point where these two semiconductors meet is known as the p-n junction.
When voltage is applied to the LED strip, the electrons from the n-type move toward the p-type holes and vice-versa. When the holes and electrons meet the p-n junction, they recombine and release energy as photons (light). As voltage is provided to the entire strip, all LEDs light up simultaneously, resulting in a continuous and uniform light source. This is how light is produced in the LED strip. You can control the brightness of the emitted light by adjusting the amount of current flowing through the LEDs using resistors or electronic dimmers.

Color Of The Emitted Light
The color of the emitted light depends on the band energy gap of the semiconductor. That is, the semiconductor material plays the main role in deciding the light color of an LED strip. The below chart shows different light colors produced due to changes in semiconductor materials-
| Semiconductor Material | Emitted Light Color |
| Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) | Infrared (IR) |
| Gallium Phosphide (GaP) | Red |
| Gallium Nitride (GaN) | Blue, Green, White |
| Indium Gallium Nitride (InGaN) | Blue, Green, Ultraviolet |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Blue, Green |
| Zinc Sulfide (ZnS) | Yellow, Orange |
| Aluminum Gallium Indium Phosphide (AlGaInP) | Red, Orange, Yellow |
Color Mixing
For RGB LED strip lights, color mixing creates the real magic. Combining the three primary colors- red, green, and blue, RGB LED strips can bring over 16 million hues! For example, if you want to create yellow light, the red and yellow diode in the LED chip illuminates with equal intensity, keeping the blue light off. Thus, yellow is created. With this principle, RGB LED strips combine color and create millions of hues. To know more about RGB lights, check this- What is RGB Lighting?
Reflection and Refraction Of The Emitted Light
The emitted light from the LED chips then passes through the encapsulation material (epoxy or silicone) of the LED strip. This diffuses and evenly distributes the light uniformly in the surrounding area. Therefore, this is how LED strip lights work.
Factors Affecting LED Strips Light Output
The light output of LED strips is affected by several reasons. The major factors are as follows-
- LED Chip & Driver Quality
The quality of the LED chip and driver can greatly impact the lighting output of LED strips. For example- if LED binning is not properly done, the LED strips won’t be able to provide the desired light color brightness or show other issues. Besides, defects in the driver can cause excess current flow that can damage the LED strips.
- LED Chip Wattage
The wattage rating determines the maximum power consumption of the LED chip. Higher wattage means brighter light. But with the increase in wattage, the heat production also increases. This eventually overheats the LED strips, which can cause permanent damage.
- Current and Voltage
LED strips have certain current and voltage requirements for optimal performance. For instance, if you input 24V to a 12V LED strip, it will potentially damage the LED strip or cause it to malfunction. This will overheat the strip and can lead to burnout or permanent damage.
- Temperature
LEDs are sensitive to temperature. Higher temperatures can damage the fixture. That is why LED strips are integrated with a heat sink that acts as a ventilator. This keeps the light fixture cool, reducing the chances of LED damage due to overheating.
- CRI
CRI stands for Color Rendering Index. It determines the accuracy of the LED light to the natural lighting. It is scaled from 0 – 100 grading; a higher grade means better color accuracy. Poor CRI rating will impact the light output. So, always keep the CRI above 80; above 90 would be best. To learn more, check this article- What is CRI?

- Color Temperature
Color temperature impacts the appearance of light color. Higher color temperature gives excellent lighting, whereas lower temperature provides warm lighting. So, when purchasing LED strip lights, you must check their color temperature. However, tunable white LED strips are an excellent choice for customizing light color temperature. To know more about this, check this article- How to Choose LED Strip Color Temperature?
- Beam Angle
The distribution of light greatly depends on the beam angle of the LED strips. A narrow beam angle provides more focus lighting. However, go for a wide beam angle to cover the border area.
- Others
Besides the facts mentioned above, the lighting output of LED strips is also affected by the LED density, chip size, diffuser, cleanliness of the cover, etc. The environment or the humidity/dust can also affect the light output over time.
Tips To Choose the Best LED Strip Lights
The requirements of LED strips vary for different applications. They come in various colors and customization facilities. However, all LED stripes are not suitable for every type of installment. So, here I bought you a quick tips segment to help you choose the best one-
- Consider the installation area before purchasing an LED strip for your project. If you want to get fixtures for outdoor lighting, choose a higher IP rating. This will protect your LED strips from adverse weather conditions like storms, wind, dust, or rain.
- Always check the voltage rating of the strips. If your input voltage exceeds the required voltage, it will damage the LED strips.
- Consider the color temperature to create a direct ambiance with your lighting. Remember, warm lighting creates a cozy environment. These are excellent for bedroom, living room, or drawing room lighting. On the other hand, cool lighting creates an energetic ambiance. They work best for task lighting.

FAQs
On average, an LED strip can last up to 50,000 hours of use. That is, you can use these lights for five to seven years at ease.
Yes, LED strips have specific points to cut. The strip will work if you cut it in the appropriate spot. However, a wrong cut will damage the circuit of the end segment. In this case, you must make another cut on the next mark.
You can make LED strip lights dimmable using compatible dimmer switches, controllers, or power supplies. But make sure the dimmer is compatible with the LED strip.
LED strip lights are designed for continuous operation and are highly energy efficient. So, you can leave them all night without worrying much.
No, LED strip lights are highly energy efficient. They consume about 85% less electricity than traditional lighting, like incandescent bulbs.
Yes, LED strips can be powered by a battery. But for this, you will require a suitable battery pack or power source and a compatible voltage and current supply.
LED strips usually take low-voltage DC (Direct Current). You’ll need a compatible DC power supply to operate them. However, some LED strips may have built-in voltage converters to work with AC power.
No, LED strip lights necessary don’t need to be plugged in. They can be powered through various means like- a power bank, solar panel, battery, etc.
The Bottom Line
LED strip lights work at low voltage, making them ideal for various applications. Whether it’s house interior or outdoor lighting, these fixtures work excellently to give a neat illumination. However, quality is important to get the best lighting output. But no worries, with LEDYi, we provide the best quality at competitive pricing. If you need a customized solution, we can help you with this, too. Besides, we have both analog and digital LED strip lights. So, whatever your requirements are, LEDYi is your ultimate solution!