Overheating of LEDs badly affects the performance and durability of the fixture. So, to ensure a proper LED functioning and thermal management system, an appropriate heat sink installation is a must. But what is a heat sink, and why is it so important for LEDs?
A heat sink is a device that dissipates heat away from the LED light source. It prevents overheating and protects the light from damage. Thus, it also expands the life expectancy of any LED.
However, there are different types of LED heat sinks. But no worries about choosing the right one, as this article will help you! So, to get an overall idea about LED heat sinks, let’s begin the discussion-
What is an LED Heat Sink?
An LED heat sink is a device that absorbs the heat generated from the LED module and transfers it to the surrounding air. It aids in the temperature regulation of LEDs and avoids overheating. That is why an LED heat sink is vital to any LED lighting system.
The heat sink is typically made of aluminum or other heat-conductive materials. It features a series of fins and ridges that increase its surface area for better heat dispersion. This large surface area allows heat to dissipate more effectively. The LED heat sink absorbs heat from the LED and transfers it to the air. This process keeps the LED cool and functioning at its best.
Why Is LED Heat Sink Important?
LED Heat Sink ensures the proper functioning and longevity of LED lights. And the LED lights emit light through the process of electroluminescence. Also, this generates heat as a by-product. This heat can cause damage to the internal components of the LED light. It also reduces its efficiency and lifespan. Here, the LED Heat Sink acts as a cooling device, dissipating the heat generated by the LED light. Thus, it keeps the internal components at safe temperatures.
The LED Heat Sink is designed with high thermal conductivity materials like aluminum. And such materials absorb and dissipate heat quickly and efficiently. It also has a large surface area that allows for maximum heat dissipation. Therefore, overheating can cause the LED light to overheat and become a fire hazard. So, it is critical to have an efficient heat sink in place.
How Does LED Heat Sink Work?
LED heat sink refers to the process of removing heat from an LED light source through the use of a heat sink. The process occurs in several stages:
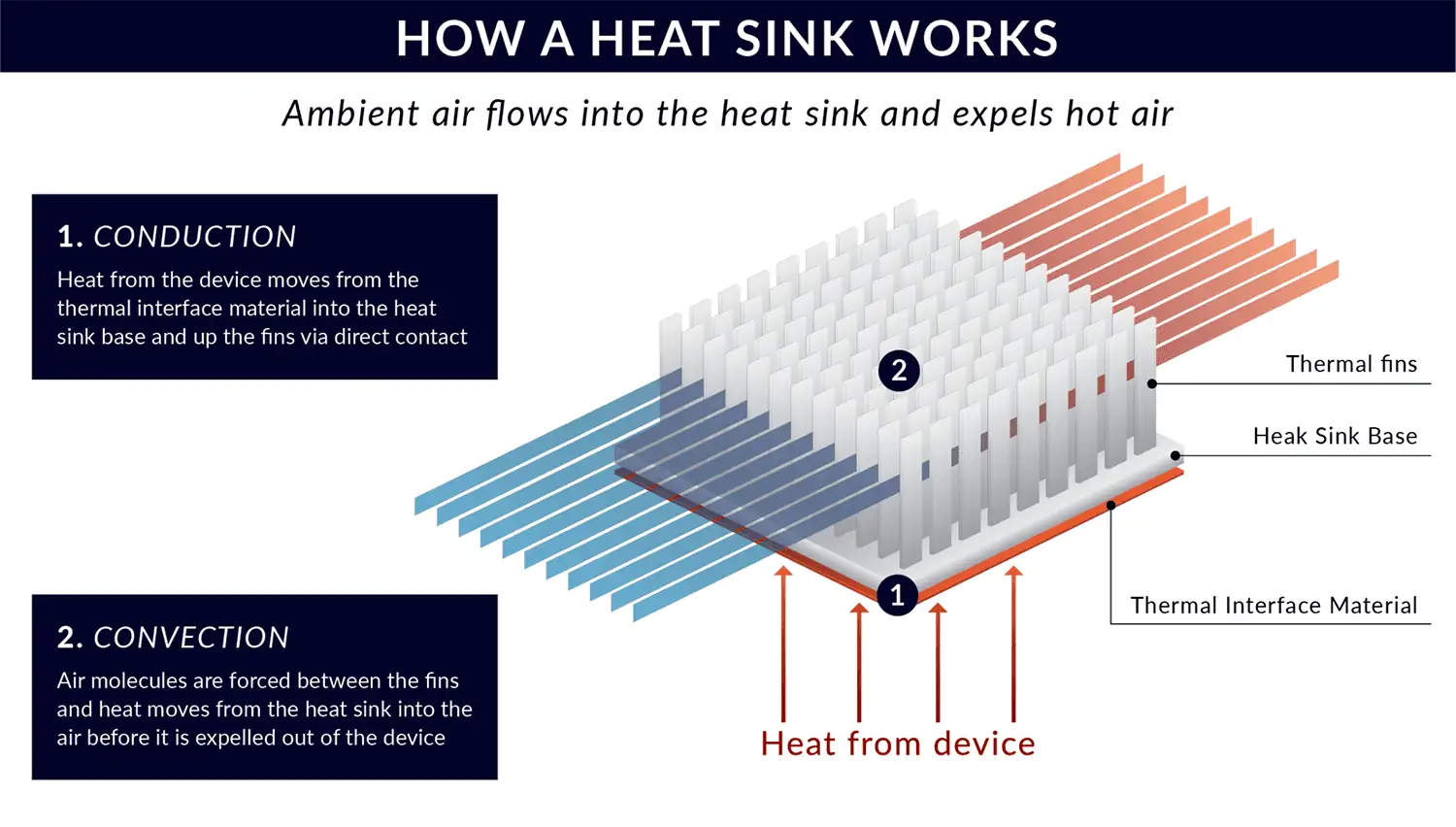
- Generation of heat
When an LED light source is powered, it generates heat as a by-product of light emission.
- Transfer of heat
The generated heat is transferred from the LED chip to the metal core printed circuit board (MCPCB) or the heat sink.
- Dissipation of heat
The heat sink is a thermal bridge between the LED chip and the surrounding environment. It conducts the heat away from the LED chip and into the air. Also, the heat sink has a large surface area, providing ample space for dissipating heat.
- Radiation of heat
The heat sink radiates heat into the surrounding environment through a combination of convection and conduction. The heat moves from the hot surface of the heat sink to the cooler air. It creates a temperature difference that drives the heat away from the LED chip.
- Cooling of LED
The LED chip temperature decreases as the heat radiates away, preventing overheating. It allows the LEDs to operate at a safe and efficient temperature. The heat sink also helps prevent damage to the LED chip, which can be caused by excessive heat buildup.
Types of LED Heat Sinks
There are several types of LED heat sinks available, including active, passive, and combination models:
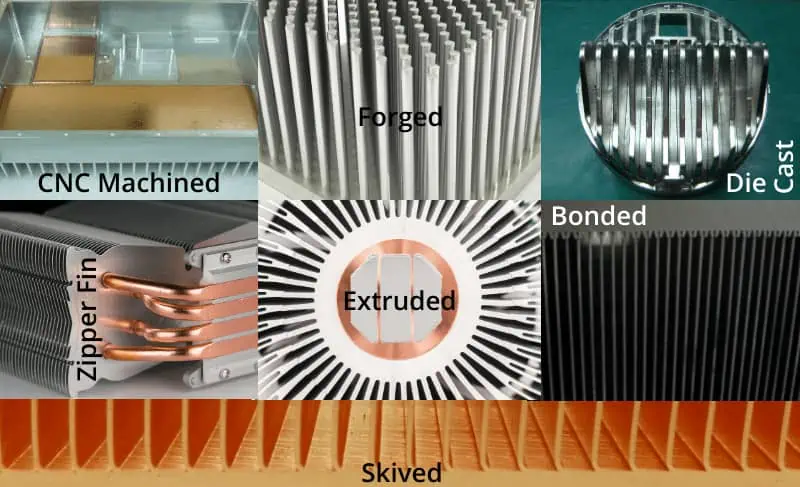
- Active Heat Sinks
An active LED heat sink is a type of heat sink that uses a fan or other mechanical means. They actively remove heat from a light-emitting diode (LED) device. And this helps to increase the performance and longevity of the LED. It further prevents overheating and prolongs the life of the LED. So, for these reasons, active LED heat sinks are often used in high-power LED applications.
- Passive Heat Sinks
Passive LED heat sinks are designed to dissipate heat generated by LED lights without using any fans or other active cooling systems. They rely on thermal conduction. The passive heat sink also depends on convection and radiation to transfer heat from the LED light source. They spread the heat into the surrounding environment.
These heat sinks are typically made of aluminum. They can also be materials with high thermal conductivity. Moreover, they feature fins and other structures. It expands the surface area available for heat transfer.
In addition, passive LED heat sinks are durable and require low maintenance. They are often used in lighting applications for their low noise levels. You can also use them for their longevity and low operating costs. Besides, they are resistant to weather and environmental conditions. So, these features make them best for outdoor lighting fixtures.
- Hybrid Heat Sinks
Hybrid LED heat sinks are thermal management devices. They combine traditional metal heat sink materials with additional elements- heat pipes, vapor chambers, or phase change materials. And the inclusion of these extra components improves the heat dissipation capability of LED lighting systems. A hybrid LED heat sink aims to efficiently remove heat generated by the LED chips, preventing thermal damage. They also improve the performance and longevity of the LED system.
- Cold Plates
Cold plates are cooling systems designed for LED lighting fixtures. They dissipate heat generated by the LEDs and maintain optimal temperature levels. These are made of aluminum and copper. It can also be a combination of both. They work by conducting heat away from the LED. Then disperses the heat into the surrounding air. Additionally, these are lightweight, efficient, and cost-effective.
- Pin-Fin Heat Sinks
Pin-fin LED heat sinks are made of a metal base plate with multiple pins protruding from the surface. This increases the surface area and promotes better heat dissipation. The pin-fin design is highly efficient at dissipating heat from the LED light source. It helps to maintain the temperature of the LED. Thus, it controls damage and improves performance. Also, these are popular in applications like high-intensity and long-lasting lighting. This can include street lighting, industrial lighting, and automotive lighting.
- Plate-Fin Heat Sinks
Plate-fin LED heat sinks consist of a base plate, a series of fins, and a heat dissipation surface. The base plate is made of a highly thermally conductive material. They provide a secure mounting platform for the LED light source. The fins are placed on top of the base plate and provide a large surface area for heat dissipation. The heat dissipation surface is typically made of aluminum. It helps to draw heat away from the LED and into the surrounding air.
Plate-fin LED heat sinks are popular in lighting applications. Because they are lightweight, have a low-profile design, and are easy to install. They also have high thermal performance and are cost-effective. This type of heat sink is also ideal for high-heat applications—for example, automotive lighting and industrial lighting.
- Extruded Heat Sinks
Extruded LED heat sinks dissipate heat from LED (light-emitting diode) lighting fixtures. They are made by extruding aluminum into a specific shape and size. It creates a finned structure that increases the surface area for heat dissipation. The heat sink is then attached to the LED fixture. This helps to keep the LED cool and increases its lifespan. Therefore, their design allows for a cost-effective and customizable solution. It is a popular choice for commercial and industrial lighting.
- Bonded Fin Heat Sinks
Bonded fin LED heat sinks consist of a base material and fins. They are bonded together using a high-strength adhesive. This bonding process helps to improve heat transfer efficiency and reduce thermal resistance.
The fins are designed to increase the surface area of the heat sink. It allows more heat to dissipate into the air. Furthermore, this helps to keep LED lights cool. Plus, it helps to prolong their lifespan and maintain their performance. Bonded fin heat sinks are typically made from aluminum or copper. They are used in streetlights, indoor lighting fixtures, and automotive lighting systems.
- Folded Fin Heat Sinks
Folded Fin LED heat sinks are a cooling system used in LED lighting fixtures. They are made of thin metal fins that are bent and stacked together. It creates a large surface area for heat dissipation. This design allows for a compact and efficient cooling solution. This is ideal for use in small LED lighting fixtures. The folded fin design also allows for good airflow. It helps to dissipate heat quickly and efficiently.
- Z-Clip Retainer Heat Sinks
Z-Clip Retainer LED heat sinks are designed with a Z-shaped clip. It attaches to the LED light and holds the heat sink in place. This allows for efficient heat dissipation. They help to keep the LED light running at optimal temperatures and extend its lifespan. LED heat sinks also come with built-in LED light retaining systems. It prevents the LED light from coming loose and improves safety.
Types of Heat Sink Materials
Heat sinks come in various materials, including aluminum, copper, and polymer.
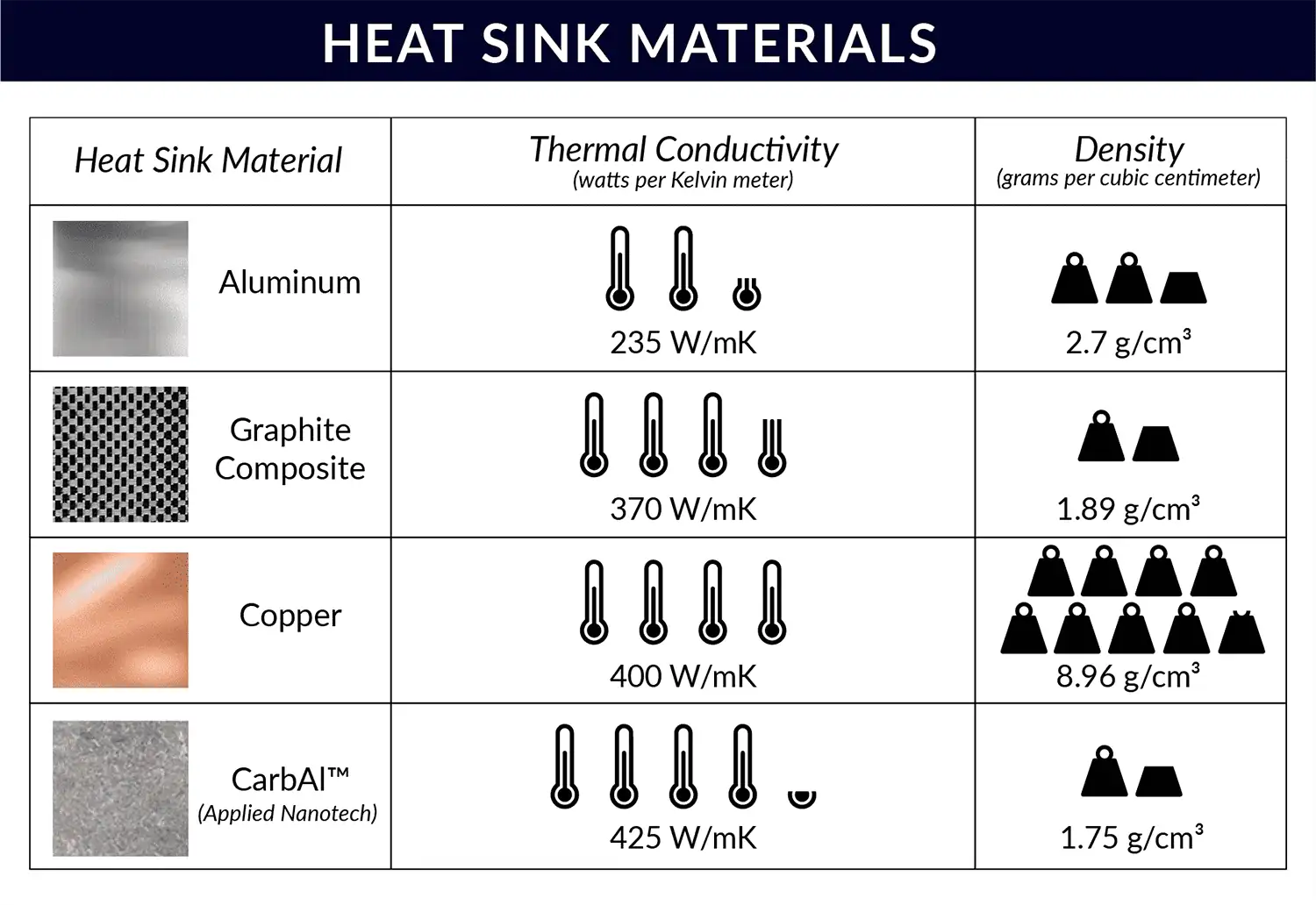
- Aluminum Heat Sinks
Aluminum LED heat sinks are a popular choice for cooling LED lighting systems. They offer several key benefits, such as low cost, lightweight construction, and good thermal performance. Aluminum LED heat sinks also dissipate heat quickly. This enables the system to run at lower temperatures and improves efficiency. Additionally, aluminum is a strong and durable material. Thus it can withstand harsh environmental conditions.
- Copper Heat Sinks
Copper LED Heat Sinks are highly efficient at dissipating heat. They reduce the risk of overheating and damage to the LEDs. Copper also has high thermal conductivity. It allows heat to be quickly transferred away from the LED. This helps maintain optimal performance over a longer period. Additionally, copper is lightweight and corrosion-resistant. This makes it a perfect alternative for industrial applications.
- Polymer Heat Sinks
Polymer LED Heat Sinks can offer improved heat dissipation. It can also provide increased efficiency and a longer lifespan for LED products. The heat sink’s unique polymer design can dissipate heat faster than traditional metal designs. This helps reduce the risk of LED failure due to thermal management issues. Polymer LEDs also require less energy to run. This makes them more cost-effective and energy-efficient.
Furthermore, LED products with polymer heat sinks have a longer lifespan than those without. This can help businesses reduce their maintenance costs. It also improves the longevity of their investments in LED lighting.
Heat Sink Materials: Aluminum vs. Copper – Which is Better?
Aluminum and copper both have their advantages and drawbacks. So it is crucial to understand their differences to make an informed decision.
| Aluminum Heat Sink | Copper Heat Sink |
| Lightweight and low cost | Heavy and expensive compared to aluminum |
| High thermal conductivity | High thermal conductivity |
| Low mechanical strength | High mechanical strength |
| Not as good at conducting electricity as copper | Excellent electrical and thermal conductivity |
Aluminum has lower thermal conductivity than copper, meaning it takes more time for heat to move through it. On the other hand, aluminum is significantly lighter than copper and has higher structural integrity.
Besides, copper has better thermal conductivity than aluminum. This makes it a better choice for applications that need the most effective heat dissipation. Additionally, copper does not corrode as aluminum does.
Ultimately, which material is better depends on the application’s specific needs. For industrial lighting and automotive lighting, copper would be best. On the other hand, aluminum is a perfect choice for architectural lighting.

Heat Sink Design Considerations
Designing a heat sink requires consideration of several factors. These are as follows-
- Type of Heat Sinks
The type of heat sink has a significant impact on the overall considerations. Passive sinks are heat sinks with a large surface area or fins. They are designed to dissipate heat through convection or radiation. Active sinks are fans or liquid cooling systems. They work by actively moving air or liquid to remove heat from the source.
Hence, each type of sink has its advantages and considerations. For example, active sinks may need extra power to operate. And it can be noisier than passive sinks. Therefore, careful consideration is a must for the different types of sinks.
- Materials Of Heat Sink
The choice of heat sink will determine the efficiency and effectiveness of the thermal management. Since each type of material has different thermal properties.
The most commonly used types are aluminum and copper. Besides, they both have good thermal conductivity. They also have a large surface area for dissipating heat. For higher temperature tolerance, other materials may require ceramic or graphite. Additionally, you must consider the heat sink’s shape and size. This ensures optimal performance and fits within any space constraints.
- Boundary Design
Boundary design affects the system’s cooling capacity, cost, and overall efficiency. Designers can optimize the thermal performance of the system. Also, the shape and size of the heat sink affect airflow, convection, and conduction. The Boundary design also impacts the surface area available for heat dissipation. A well-designed heat sink will have enough surface area. It will dissipate the generated heat effectively while minimizing overall costs.
MCPCBs: How It Helps the LED Heat Sink?
MCPCBs are metal-core printed circuit boards. They are designed to dissipate LED heat away from the light source effectively. The metal core of the MCPCB acts as a thermal bridge. This allows heat to dissipate from the LED to the heat sink.
MCPCB technology takes advantage of the fact that metal has a much higher thermal conductivity than FR4 (fiberglass-reinforced epoxy). Thus, it more effectively transfers heat away from LEDs. The metal core also provides structural stability. It improves electrical connectivity, making it an ideal solution for LED cooling applications.
Do LED Strips Require Heat Sink?
Small, low-powered LED strips do not typically require a heat sink as they generate very little heat. However, for high-powered LED strips, a heat sink is highly recommended. As it helps dissipate heat and prevent damage to the LED strip.
Heat sinks are often constructed of metal and serve as conductors. It pulls heat away from the LED strip and dissipates it into the surrounding air. Without a heat sink, high-powered LED strips can overheat. This will reduce their lifespan and cause them to fail. So, if you are using a high-powered LED strip, it is advisable to use a heat sink. This will ensure its longevity and optimal performance.
How To Size A Heat Sink For Strip Lights?
Sizing a heat sink to strip lights is a crucial step for the longevity and efficiency of the lighting system. Here are the steps to size the heat sink for strip lights:
Step-1: Determine the power of the strip lights
The first step is determining the power of the strip lights in watts. This information is usually available in the product specifications.
Step-2: Calculate the heat generated
The next step is calculating the heat generated by the strip lights. This can be done using the formula: Heat Generated = Power x Efficiency. The efficiency factor is usually around 90%.
Step-3: Determine the thermal resistance of the heat sink
Thermal resistance is a measure of the resistance of the heat sink to heat transfer. It is usually expressed in °C/W.
Step-4: Determine the maximum allowable temperature rise
The maximum allowable temperature rise is the difference between the ambient and maximum temperatures the strip lights should reach. The manufacturer usually specifies this temperature.
Step-5: Calculate the required heat sink size
The final step is calculating the required heat sink size using the formula-
Required Heat Sink Size = Heat Generated ÷ (Thermal Resistance x Maximum Allowable Temperature Rise)
It is important to remember that the calculations above are simply estimations. For a precise estimate, you can speak with an expert. Additionally, consider the physical dimensions of the heat sink. These are the length and width to ensure that it fits appropriately in the lighting system.

Factors to Consider When Choosing a LED Heat Sink
The factors that should be taken into consideration when choosing a LED heat sink are as follows:
Thermal Resistance
Thermal resistance refers to the ability of the heat sink to dissipate heat away from the LED. If the thermal resistance is too high, heat will build up and cause the LED to overheat and fail prematurely.
On the other hand, if the thermal resistance is too low, the heat sink will be too bulky. This will affect the overall design of the LED system. It’s essential to strike a balance between thermal resistance and other factors, such as cost, size, and material, to choose the right LED heat sink for your specific application.
Heat Flow
When selecting an LED heat sink, consider the heat flow. The heat sink’s primary function is to dissipate heat away from the LED. It prevents overheating and extends its lifespan. If the heat sink cannot effectively transfer heat, the LED will eventually overheat and fail.
You should evaluate the heat flow based on the LED’s power output. It also counts on the ambient temperature and the material’s thermal resistance. Choosing a heat sink with high thermal conductivity and low thermal resistance is recommended. This will ensure optimal heat transfer. With proper heat flow, the LED heat sink will provide reliable and efficient cooling for the LED.
Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity is the ability of a material to transfer heat from one point to another. High thermal conductivity means the heat will efficiently dissipate from the LED to the heat sink. Using a heat sink of better thermal conductivity prevents LEDs from overheating. However, different materials have different thermal conductivity capacities. For example, aluminum’s thermal conductivity ranges from approximately 170-251 W/mK. At the same time, copper’s thermal conductivity is higher than aluminum’s, with a value of roughly 401 W/mK.
Perfect Heat Sinks Type
Passive heat sinks are designed to dissipate heat through natural convection and conduction. Hence, they do not rely on active cooling methods such as fans or water cooling. This can be an attractive option for some applications as it eliminates the need for maintenance and noise. It also stops potential failure points associated with active cooling. Additionally, passive heat sinks can be more cost-effective. It also has a smaller form factor than dynamic cooling solutions.
Natural Convection
Natural convection refers to the flow of heat transfer through a fluid, usually air. In this process, the fluid/air flowing across the warm heat sink removes heat from the surface and transfers it into the surrounding environment.
However, increasing the air turbulence between the fin spacing of the heat sinks greatly enhances natural convection. In this case, the design and structure of fins/plates matters. For example- fins with drilled holes accelerate the cooling mechanism. So, consider this factor before choosing an ideal heat sink for your LED.
High Heat Dissipation
High heat dissipation allows the LED lights to operate at a lower temperature. It reduces the risk of damage from overheating and increases the lifespan of the lights. And this type of heat sink reduces the energy required to cool the lights. It, in turn, reduces overall energy consumption. Also, a high heat dissipation heat sink helps to reduce maintenance expenses in the long run.
Shape and Size of Fins
The size and number of fins will determine the surface area for heat to dissipate. At the same time, the fins’ shape can affect the heat sink’s airflow and overall efficiency. Besides, a heated sink with large, evenly-spaced fins will provide better heat dissipation. Compared to one with small, closely spaced fins. Additionally, the shape of the fins, such as flat or curved, can also influence the heat dissipation performance.
How To Install a LED Heat Sink?
Here is a step-by-step guide to installing a LED heat sink:
Firstly, prepare the LED for heatsink installation. If the LED is new, insert it into the LED holder or socket. If the LED is installed, ensure it’s securely in place and won’t come loose during the heat sink installation process.
Secondly, clean the LEDs and heat sink’s surface with isopropyl alcohol to ensure a strong bond. Apply a small amount of thermal compound to the surface of the LED. This inclusion will improve the heat transfer between the LED and the heat sink.
Thirdly, align the heat sink with the LED and attach it to the LED holder or socket. Depending on the heat sink and LED holder’s design, this may involve screws, clips, or a combination of both. Once the heat sink is securely attached, turn on the LED and check for proper operation. The LED should be bright and stable without any flickering or dimming.
Finally, if the LED works properly, tighten any screws or clips to ensure a secure connection. If necessary, add a thermal compound to improve heat dissipation.
How to Maximize the Efficiency of Heat Sink?
It’s vital to ensure that it is correctly sized to maximize the efficiency of an LED heat sink. Also, adequately constructed and suitably installed. Verify that the heat sink is large enough to withstand the heat generated by the LED device. If it is too small, it won’t dissipate heat effectively. Additionally, selecting a high-quality material with good thermal conductivity is a must. This will help to ensure optimal performance.
Finally, proper installation is essential for optimal performance. Ensure the LED heat sink is securely attached to the device. Also, ensure that there are no gaps in the assembly that could interfere with airflow. These steps will help ensure that your LED heat sink operates efficiently.
Does the Weight of the Heat Sink Matter?
Yes, the weight of the heat sink does matter. The heavier the heat sink is, the better it will dissipate heat and keep the components cooler. Heavier heat sinks also have more surface area. This allows them to absorb more heat from the components they are cooling. So when choosing a heat sink, it’s essential to consider its size and weight.
FAQs
Most LED heat sinks are not waterproof. However, some LED lights are designed with waterproof heat sinks. So you can use them in damp environments. It is essential to check the specifications of the LED light to determine if it is designed for use in a waterproof environment.
Maintaining an LED heat sink is relatively easy. Regularly inspect the heat sink for any signs of dust, dirt, or debris buildup. Then clean it as needed to ensure its efficient performance. Additionally, you should check the fins periodically. This ensures they are still in good condition and not bent or broken. Lastly, always use a thermal compound when attaching the LED heat sink to its mounting surface.
The maximum temperature varies depending on the type of heat sink and the ambient temperature. Check with the manufacturer for the specific temperature range for each individual product. The maximum temperature may vary depending on the particular product. But generally, it should not exceed 80°C.
Yes, a simple inspection can determine whether it is functioning correctly. If the heat sink appears in good condition with no damage or signs of wear, it is likely working correctly. Also, checking the temperature of the heat sink is a simple and effective method.
It is recommended to use thermal paste with an LED heat sink. It helps with better heat dissipation and ensures the maximum efficiency of the LED.
Yes, there is a difference between metal and aluminum LED heat sinks. Metal LED heat sinks are usually heavier and more durable, while aluminum LED heat sinks are lighter and less expensive.
Yes, the LED heat sink should be regularly inspected and maintained. It is crucial to check for any obstructions that may impede airflow. Also, ensure that the heat sink remains securely fastened. You should occasionally replace the thermal paste between the LED and the heat sink.
Conclusion
Overall, LED heat sinks are specifically designed for LED lighting. It provides a way to keep LEDs running at their best while also keeping them from becoming too hot. They work by transferring the heat away from the LEDs. This allows them to be cooler and more efficient.
In conclusion, an LED heat sink prevents any potential damage that can be caused by overheating. Without it, LEDs would not be able to reach their full potential. Therefore, ensuring proper heat management is essential for any LED setup.
LEDYi manufactures high-quality LED strips and LED neon flex. All of our products go through high-tech laboratories to ensure the utmost quality. Besides, we offer customizable options on our LED strips and neon flex. So, for premium LED strip and LED neon flex, contact LEDYi ASAP!



