Looking for a cost-effective LED dimming solution that is compatible with your existing electrical setup? TRIAC dimming is the go-to option!
TRIAC dimming is an analog and easy-to-use dimmer that requires no special setup. Though these dimmers were typically designed for incandescent and halogen bulbs, LED-compatible TRIAC dimmers are also available. They support higher voltage and are cheaper than other dimming technology. You will also find a variety of dimmer switch options that are compatible with TRIAC dimming.
In this guide, I am going to present you with in-depth details about TRIAC dimming, its pros and cons, its working mechanism, and more. At the end of the guide, I have also added a comparison between TRIAC and other dimming options. So, let’s dive into the discussion:
What Is TRIAC Dimming for LEDs?
TRIAC dimming, popularly known as a phase-cut dimmer, is a brightness-controlling method for LED lights. It uses a semiconductor device known as TRIAC. TRIAC stands for “Triode for Alternating Current.” It is an electronic component with three terminals that can conduct current in either direction when turned on. TRIACs were developed to facilitate the management of AC power. It acts as a switch and can control the current, dimming or brightening the lights.
Earlier, configuring LEDs with this TRIAC was challenging; it was mostly compatible with incandescent lights. However, with the advancement of technology, TRIAC dimming drivers have been tailored specifically for LEDs. It supports a wide range of voltage and current options without harming the LED. However, they are sensitive to high currents. Compared to Silicon Controlled Rectifiers (SCRs), TRIACs have a lower current rating of less than 50 A. Nevertheless, SCRs are not as effective as TRIACs at managing low power in AC circuits. Besides, TRIAC is easier to use than SCRs. It can handle both positive and negative voltage across its terminals, which makes TRIAC dimming a handy tool.
What is A Dimming Curve?
The dimming curve is the graphical representation of how a dimmer brings changes in the light output. It shows the relationship between the input control signal and the resulting light output in dimming devices. While buying dimmers, you must consider the dimming curve as it affects the light output. It is also the physical representation of how the digital dimming equipment works.
Types Of Dimming Curve
Based on how they look, dimming curves can be of different types. We’ll talk about the main types of dimming curves (sometimes called “square-law” dimming)- linear dimming curve and the logarithmic dimming curve.
a. Linear dimming curve
When using linear dimming curves, the amount of light that comes out is directly related to the amount of energy that goes into the system. The strength of the input signal, which in this case is 25%, will be exactly the same as the output value.
b. Logarithmic dimming curves
In logarithmic dimming curves, the values of the inputs change as the dimming levels go up. When the brightness is lowered, the signal sent to the driver will change more slowly. But when the brightness is raised, it will change more quickly.
A dimmer, which is an input device or a driver, can have any curve programmed into it, such as an “S” curve, a “soft linear” curve, etc (an output device). This type of input range, which is also called a “slider,” is usually meant to give you more precise control over a portion of the total input range.
However, you can tell the manufacturer that you want “linear” or “logarithmic” for all the input and output devices. This will bring you the best possible results.
How Does The TRIAC Dimming Work For LEDs?
The TRIAC dimmer is installed between the power supply and the LED fixture. The power delivered to the LED is controlled by the dimmer, which brightens or dims the light. It cuts the AC voltage into many small segments, and each of these parts is half a sine wave.
TRIAC is a three-pin power electronic circuit element that can alternate current. The three pins are named as-
- Main Terminal 1 (MT1)
- Main Terminal 2 (MT2)
- Gate (G)

Considering the internal structure, TRIAC dimming consists of common gate pins and two thyristors arranged in reverse parallel. Due to having a single gate, it can accept current in both directions. Besides thyristors, basic devices like capacitors and potentiometers work together to dim the light. Here is an in-depth description of TRIAC dimmings’ mechanism:
Thyristor Activation
The thyristor is a three-terminal semiconductor- two main terminals and one gate. It is activated when a small trigger of electric current is delivered to the gate. Once it is activated, it opens up the gate and passes current to two main terminals. This trigger of current is supplied in small intervals. As it comes in contact with the current, the gate opens, and when no current is delivered, it closes. Likewise, the gates close and open 50 times in a second. This way, thyristors make the current flow in small pulses instead of a continuous flow.
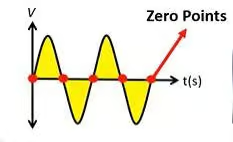
However, the timing of the gate trigger affects the flow of current that is responsible for dimming or brightening the light. If the gate is triggered at the beginning of the sinusoidal cycle, that is, near the start of the wave, more current can pass. As a result, the light becomes brighter. In contrast, if the gate is triggered at the end of the sinusoidal cycle, less current flows dimming the light.
Capacitors Charging Cycle
A capacitor controls the opening and closing of the thyristor’s gate. It stores electrical energy. When it is in charging mode, the gate remains closed, preventing current from reaching the main terminals. Once the capacitor gets fully charged, it opens the gate, allowing the current to flow, and thus, the light glows up. The duration of charging depends on the capacity of the capacitor. Large capacitors have high capacity and take more time to charge.
Resistance Tuning with Potentiometer
TRIAC dimmer doesn’t have a digital controller. A variable resistor, potentiometer and capacitor control the timing of the gate trigger. The potentiometer comes in the form of a knob or dial. When you adjust the potentiometer, the resistance of the TRIAC dimmer changes. As a result, the amount of current flow in the capacitor also changes. This affects the duration of the pulses at the light source.
TRIAC Dimmer Control
The TRIAC difference takes the input voltage from the power source and converts it into short pulses via the potentiometer and capacitor. For longer pulses, the flow of current increases and the light output is brighter. Again, for short pulses, the flow of current decreases, dimming the light. This way, the TRIAC dimmer allows you to control the brightness of the LED lighting.
How Does TRIAC Dimming Benefit LED Lights? – Advantages
High Voltage Support
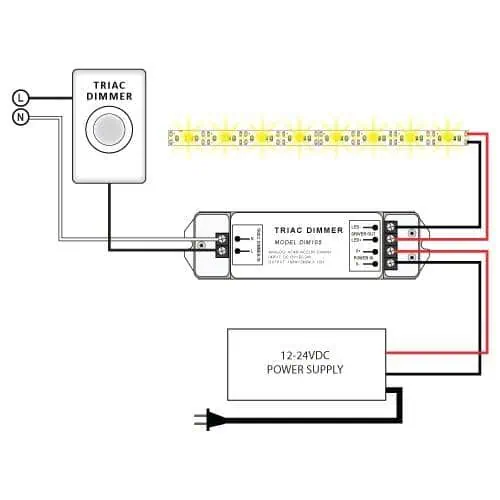
Though TRIAC dimmers are sensitive to high currents, they support high voltage (between 100-240V AC). So you can use them both for residential and commercial purposes. However, to deal with high voltage while using low voltage LED fixtures, TRIAC dimmer often needs additional components like an LED driver. For instance, in LED strip lights, the dimmer must include an LED driver to convert the high-voltage AC to low-voltage DC.
Smooth Dimming Control
TRIAC dimmer offers you precise control over the brightness of the LED lights. All you need to do is adjust the control knob or the potentiometer, and the light will dim or brighten up accordingly. For instance, turning the controller up or rotating clockwise will increase the brightness. Similarly, moving the knob down or rotating it anticlockwise will dim the light. This way, anyone can use a TRIAC dimmer to control light brightness without requiring any technical knowledge or using additional devices.
Reliability
TRIAC dimmer is an analog technology, so there are no worries of getting hacked or having future incompatibility. You can hardwire the dimmer switch into your wall sockets and use them for years without any upgrading requirements or replacement.
Compact Size & Simple Installation
The compact size of the TRIAC dimmer allows you to install them in tight spaces. The installation process is also pretty simple. They come in single units, and you can install them in the pre-existing house wiring with ease.
Cost-Effective
Compared to other dimming options, TRIAC dimmer is more cost-effective. It has a basic composition consisting of a thyristor, a capacitor, and a potentiometer. The major cost of a TRIAC dimmer basically depends on its fancy dimmer switch and housing. So, by choosing a simple switch design, you can save costs. This makes the TRIAC dimmer suitable for houses, offices, warehouses, etc.
Drawbacks Of Using TRIAC Dimming With LED Lights – Disadvantages
Potential Flickering and Humming
The frequent on & off action or fast cycle of TRIAC dimmers can damage the internal components of LEDs. This leads to flickering issues in the LEDs. Besides, it also leads to a humming sound that definitely affects the lighting experience.
Potential Lifespan Reduction
An incompatible TRIAC dimmer can badly affect the lifespan of the LED lights. Again, the rapid switching function of this dimmer can damage the LED and also overheat them, reducing the lifespan.
Weaker Dimming Drives & Limited Dimming Range
The TRIAC dimmer is only limited to the AC cycle and works with AC LED lights. Besides, like other advanced dimming options, it can’t completely stop the current flow. As a result, a small amount of current still flows even at the lowest setting. This limitation is noteworthy for applications that require precise control mover like brightness, for example, lights in theater.
Less Energy Efficiency
TRIAC dimmer doesn’t use all the power drawn from the wall socket. Only a small amount of it is passed to the LED to reduce its brightness. Besides, when using TRIAC dimmers with high voltage LED fixtures, some energy is also lost, such as heat and other devices within the TRIAC. This makes them more energy-inefficient compared to other dimming technologies like PWM.
Type of TRIAC Dimmer: Leading Edge & Trailing Edge
Based on the different dimming methods in the positive half-cycle and negative half-cycle, the TRIAC dimmer can be of two types:
1. Leading-Edge Dimming
Leading-edge dimming is also known as forward-phase dimming. In this method, the dimming in the AC begins at the start of the positive half-cycle. That is, the current flow is stopped right after it crosses zero, and the AC waveform starts. This creates a small pause before the current reaches the fixture.
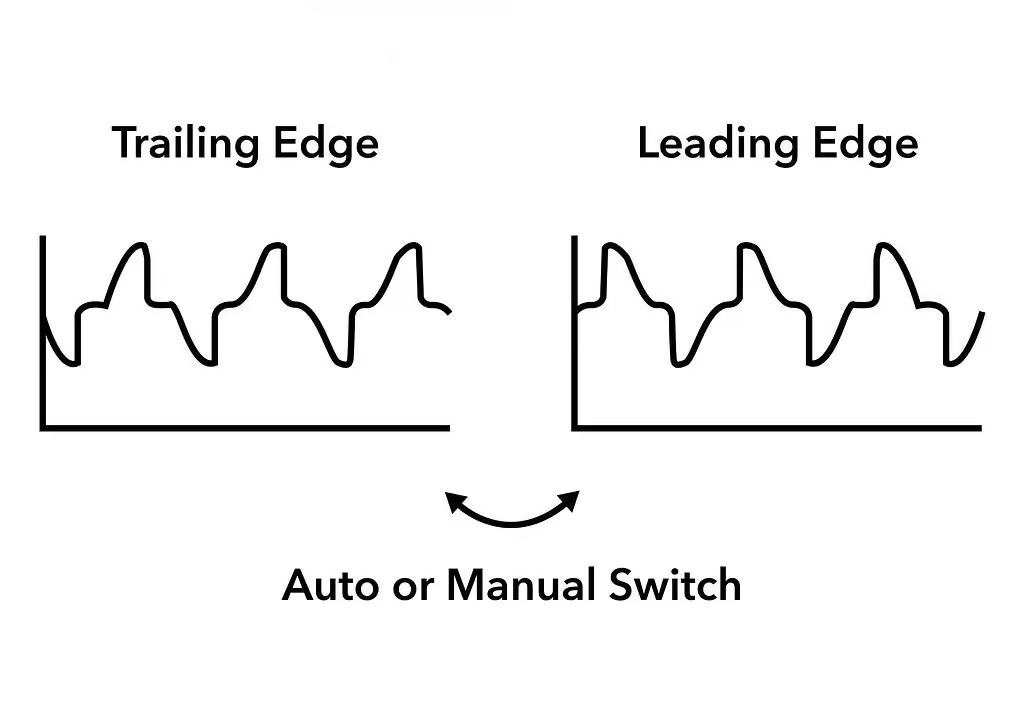
2. Trailing-Edge Dimming
Trailing-edge dimming is also known as reverse-phase dimming. Here, the dimming of the AC starts at the end of the positive half-cycle. That is, the flow of current stops right before it crosses zero, and the AC waveform ends. In this method, to dim the light, the magnitude of the current gradually falls down from the maximum value.
Differences Between Leading-Edge and Trailing-Edge Dimmers
Leading-edge dimmer switches are easy to install and have a simple configuration. This is why these were used to dim incandescent, halogen, or wire-wound magnetic transformers. Besides, these dimmers are also more affordable than trailing-edge dimmer switches. Leading-edge dimmers have a high minimum load, but new or recent light fixtures use low power. That is why the leading-edge dimmer switches are no longer compatible with modern low-power light fixtures like LEDs or CFLs.
In contrast, the functionality of trailing-edge dimmers is more complex than the leading-edge ones. They have a lower minimum load and are suitable for dimming lighting circuits with smaller, less powerful bulbs. Additionally, trailing-edge dimmers run quieter and smoother than leading-edge ones. They are also less prone to flickering and overheating. These are widely used to control residential and commercial lighting. However, trailing-edge dimmers are expensive compared to the leading-edge dimmers.
| Criteria | Leading-Edge Dimmers | Trailing-Edge Dimmers |
| Direction of Dimming | Forward phase dimming cuts the front part of the AC waveform | Reverse phase dimming cuts the end part of the AC waveform |
| Technology | Old | New |
| Load Requirements | Requires large minimum loads to operate efficiently | Works better with low-wattage loads. |
| Compatible With | Traditional light fixtures like- incandescent and halogen bulbs | Low-voltage lighting like LED and CFLs |
| Functionality | Simple | More complex |
| Energy Efficiency | Less | More |
| Electrical Noise | Produce more noise | Quicker and smoother |
| Cost | Cheaper | Expensive |
Which TRIAC Dimmer Is Suitable For LED: Leading-Edge Or Trailing-Edge?
Leading-edge dimmers were actually designed for high-power consumption bulbs like incandescent and halogen. As LED lights use less power, they are not compatible with leading-edge dimmers. In fact, LED lights don’t have the minimum load required to use them with such dimmers. Therefore, if you use leading-edge dimmers with LED, it will face flickering and humming issues.
Trailing-edge dimming is ideal for LED lights as they are compatible with low-power consumption bulbs. However, while dimming LED lights with a trailing edge dimmer, you must follow the 10% rule. According to this rule, this dimmer can only use 10% of its full capacity while controlling LED lights. For example, if a trailing edge dimmer with 400W of capacity can easily handle 400W of incandescent bulbs, it can handle only 10W of LED fixtures. That is to say, a 400W dimmer can only control a maximum of 40W of LED lights.
Nevertheless, trailing-edge dimmers manage low-wattage loads in the best way possible. Therefore, you need not worry about the large minimum load that leading-edge dimmers require. You can use as many LEDs as you want to get the effect you want. This makes trailing-edge dimming suitable for LED lights in comparison to leading-edge dimming.
Types of TRIAC Dimmer Switches
a. Single Pole Switches
Single pole switches are the most common TRIAC dimmer used in houses or residential uses. To control the brightness, they come with a slider, dial or on/off button. Single-pole switches have the most basic configuration compared to other dimmer switches. It features a three-wire design composed of a hot, a neutral, and a ground wire. However, it can control only one light fixture from a single location.
b. 3-Way/4-Way Switches
3-way switches have a more complicated configuration than single pole switches. It has a four-wire design- a hot wire, a grown wire, and two traveler wires. These travelers’ wires are connected to another switch at a different location. This allows the 3-way switches to control one or more fixtures from two different locations.
4-way switches are ideal for large spaces that require multiple light controlling points. It allows you to control lighting from three different switches/locations. However, the 4-way switches don’t connect directly with the fixture. Instead, they are used in combination with two 3-way switches acting as a bridge.
c. Multi-Location Switches
Multi-location switches are advanced versions of 4-way switches that allow you to control the lighting from more than three locations. Using these switches, you can have two different dimmings active in your room. This makes them suitable for applications that require precise and greater control over lighting.
d. Plug-in Switches
Plug-in switches are a portable solution for TRIAC dimming. It is designed for lamps or fixtures that are plug-in into power outlets. To add dimming capability to such fixtures, you need no hardwiring hassles. Just wire a plug-in dimming switch into the wall socket, and you can control the lights. However, make sure the LED lights used in the lamps are dimmable to connect to the plug-in switches.
e. Smart Switches
Smart switches offer you the highest flexibility in controlling the light fixtures. They have a built-in transmitter that connects to your smartphone. You can control the light with your phone from anywhere via an internet connection. That is, even if you are not at your house, you can still control the lighting of your house from outside. Besides, it allows advanced features like timer settings. You can set turn-on and turn-off time schedules via the compatible app on your mobile phone. The lights will automatically turn on or switch off as per the schedule.
How to Choose the Right TRIAC Dimmer For LEDs?
You must consider the below factors to ensure the TRIAC dimmer you purchase works effectively with your LED lighting:
Bulb Type & Compatibility With LED
Remember, TRIAC dimmers are mostly designed for traditional fixtures like incandescent and halogen bulbs. If you are planning to use it with LEDs, make sure the dimmers are compatible with LED lights. Besides, the light must be dimmable. Using a TRIAC dimmer with LED light that is not dimmable will reduce the lifespan of the fixture. Besides, it will cause flickering issues and performance problems.
Load Capacity
LED lights consume low power in comparison to incandescent and halogen bulbs. Therefore, you must use a trailing-edge TRIAC dimmer that works with a low minimum load requirement. Avoid using a leading-edge TRIAC dimmer with LED light. They are designed for bulbs with high power consumption and are not suitable for LEDs.
Dimming Range
Compared to other dimming options, TRIAC dimmers have a limited dimming range. Due to incompatibility, the LED may not dim down to zero. Thus, you will not get the expected result. So, better check the specification of both the LED and the TRIAC dimmer to ensure you get the desired dimming range.
Features
Want smart lighting features in your house? Convert your house to a smart home with TRIAC dimmers that have built-in features for smartphone connection. These dimmers integrate with apps and allow you to control the LED lights using your smartphone from any place. You can also look for intuitive controlling features in the TRIAC dimmer. For instance, consider features like sliders or touch interfaces for easy and more precise control.
Installation Requirements
Some TRIAC dimmers may require a neutral wire, while others may not. Therefore, you must check if the wiring of your existing switch box matches the dimmer. Besides, the installation process of TRIAC dimmer depends on the light controlling requirement. For example- if you want multi-location control over the lights, you will need a multi-location dimmer switch or setup like 3-way or 4-way switches. Besides, the space and size of the TRIAC dimmer also matter. You must make sure the dimmer you purchase must fit into the switch box without overcrowding it.
AC Dimming vs. DC Dimming: Know Your LED Requirements
TRIAC dimmers operate at AC current and are primarily designed for incandescent bulbs and some compatible LED lights. However, some LED lights, like LED strips, usually operate at AC. In this case, it is better to choose a DC dimmer. If you use a TRIAC dimmer with AC LED strips, make sure it has a built-in driver that converts the AC to DC before passing the current to the fixture.
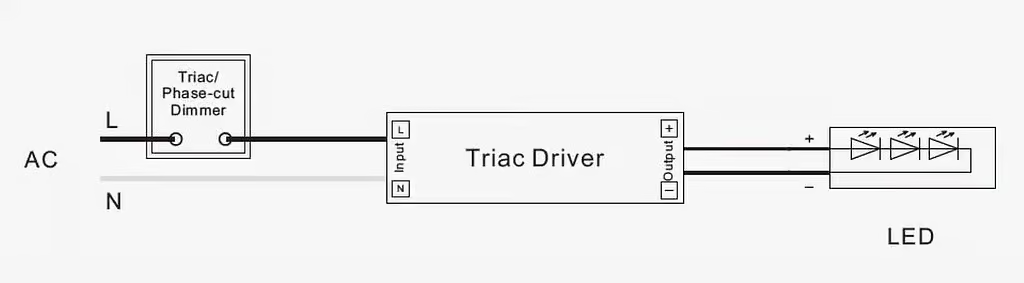
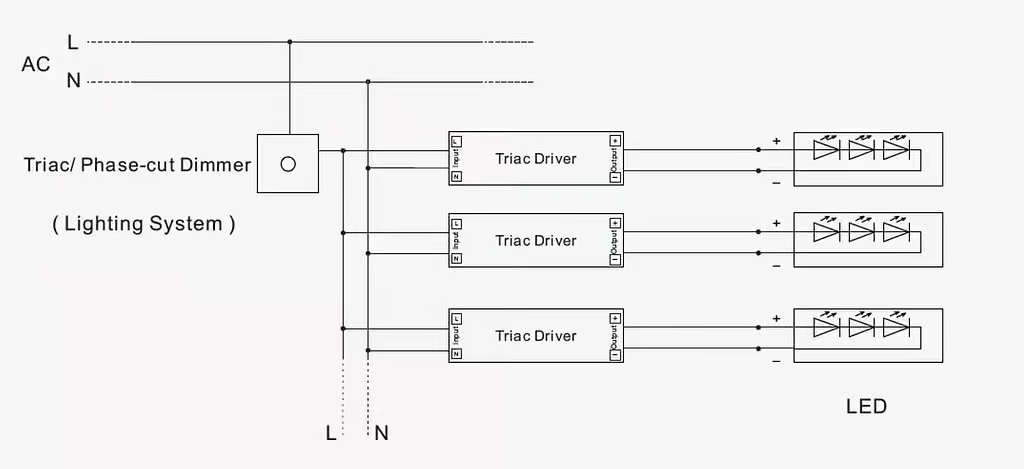
TRIAC LED Control System And Its Wiring
The TRIAC is a semiconductor device with three terminals- one gate and two main terminals. To turn it on, you must apply a voltage to its gate terminal. The dimmer turns off as you remove the voltage from the gate. Therefore, this dimmer is ideal for applications where you need precipice control over the current flow in LEDs.
To start the installation process of the TRIAC dimmer, you first need to remove the existing standard light switch. Once you have removed it, connect the black wire of the dimmer to the black wire coming out of the wall outlet. Similarly, connect the white wire of the dimmer to the existing white wire of the wall.
Lastly, connect the bare copper ground wire of the wall to the green ground wire on the dimmer, and it’s done. This way, you can quickly and easily wire the TRIAC dimmer.
TRIAC Controller & Receiver
TRIAC controllers let you change many aspects of the lighting. They achieve the effect of a dimmer setting by quickly reversing the flow of electricity, which is how they work. It applies to LEDs and other forms of lighting technology in the same way. TRIACs are usually used in high-power situations, such as when lighting, heating, or controlling motors. They turn electricity on and off more quickly than regular power switches. Thus, it helps cut down on noise and EMI that would otherwise be present.
On the other hand, using a TRIAC receiver, you can modify the quantity of power sent to a load. In order to accomplish this, it maintains a tight watch on the voltage present between the terminals of the TRIAC and activates the load. It is done when that voltage reaches the threshold that has been set. This receiver can be used in a variety of different ways. Some examples of these are adapters for power outlets, throttles for motors, and dimmers for lights.
TRIAC Dimming Vs. Other Dimmers
Besides TRIAC, there are many other types of dimmers available to control lighting. Here, I’ve included a side-by-side comparison of TRIAC dimming with other variants to help you pick the best one:
TRIAC Dimming vs 0/1-10V Dimming
Like TRIAC, a 0-10V system is an analog dimming method. The driver in it has two extra ports for +10V and -10V. However, a traditional Triac dimmer only has one port for +10v and -10v.
The 0/1-10V dimming switch controls the light electrical signals between zero and ten volts (for 0-10V dining) and from one to ten volts (for 1-10V dining). In this case, 0V results in a complete blackout, and 10V is the highest brightness level. In 1-10V dimming, the output current is 10% when the voltage is at 1V, and it is 100% when the voltage is at 10V. In contrast to 0–10V, which has a built-in on/off switch, 1–10V does not. Therefore, you can not turn off the light completely with 1-10V dimming, but you can do it with 0-10V dimming.
| Criteria | TRIAC Dimming | 0/1-10V Dimming |
| Circuit | AC power | DC power |
| Dimming Principle | To achieve dimming, TRIAC changes the current by regulating the voltage by either a negative half-cycle (trailing edge dimming) or a positive half-cycle (leading edge dimming). | It adjusts the brightness of the light by adjusting the input 0/1-10V DC voltage. |
| Controlling Mechanism | Uses a thyristor | Controls the voltage for dimming |
| Controlled Lighting System | Small | Large |
| Wiring | No extra wiring is required; uses standard electrical wiring. | Requires additional control wires (+ and -) to adjust brightness. |
| Applications | In lighting, electrical appliances, etc. | High-power uses and applications that require precise dimming, e.g., stage lights. |
TRIAC Dimming vs PWM Dimming
PWM stands for “Pulse-Width Modulation”. Unlike analog TRIAM dimming, PWM has digital dimming technology. This is an effective method to control analog circuits that use the digital output of a microprocessor. Measuring the intensity of analog signals is also easy with pulse-width modulation (PWM). You can manipulate the duty cycle of the square wave by using high-resolution counters.
The PWM signal remains digital even when the full-scale DC supply is not always present. When the light is connected to the DC supply, it turns on. Again, when there is no DC supply, the power cuts off, the light stops receiving the signal, and it turns off.
PWM is used in many fields; for example- it is used in measuring, communications, power control and conversion, and LED lighting. It is easier to use and is compatible with most of the lighting. That is because most modern microcontrollers and DSPs have PWM controllers built right into the chip. This makes digital control more convenient in general to TRIAC dimming, which is not compatible with all LEDs. Besides, you can cut off the energy cost by switching an analog TRIAC dimmer to a digital PWM dimmer.
| Criteria | TRIAC Dimming | PWM Dimming |
| Full-form | TRIAC stands for “Triode for Alternating Current.” | PWM stands for “Pulse-Width Modulation.” |
| Dimming Technology | Analog | Digital |
| Type | Phase-cut dimming (AC dimming) | DC dimming |
| Energy Efficiency | Low | High |
| Compatibility | Works with incandescent, halogen, and some dimmable LED lights. | Used with LED drivers and low-voltage LED lights. |
| Light Off Control | Switches off the light by cutting all power | Turn off the light by setting the duty cycle to 0% (no pulses sent). |
| Dimming Performance | Varies for different lights; it may not be smooth for all LEDs | Smother and non-flickering free dimming. |
TRIAC Dimming vs DALI Dimming
DALI is not exactly a dimming method but a digital light-controlling technology based on the DALI protocol. DALI stands for “Digital Addressable Lighting Interface.” compared to TRIAM dimming, DALI is more advanced and offers greater light-controlling flexibility. It offers precise and addressable control over the LED. Besides just dining the lighting, you can also adjust the color temperature of the LED fixtures using DALI dimming. This makes them a popular option for controlling tunable and RGBW LED lights.
| Criteria | TRIAC Dimming | DALI Dimming |
| Full-Form | “Triode for Alternating Current.” | “Digital Addressable Lighting Interface” |
| Type | Phase-cut (AC dimming) | Digital communication protocol (DC dimming) |
| Dimming Mechanism | Cuts a portion of the AC waveform to reduce power | Sends digital commands to adjust light intensity |
| Wiring | Requires no extra control wires | Requires dedicated DALI control wires for communication |
| Energy Efficiency | Less | Hight |
| Lighting Scenes | Not supported | Supports |
| Scalability | Limited | Highly scalable; ideal for large and complex installation |
| Cost | Cheap | Very expensive |
Industrial Grade Alternatives to TRIAC Dimmer
DMX Dimming
DMX stands for “Digital Multiplex Signal”. It is a digital protocol that controls multiple light fixtures or channels from a single location. Compared to TRIAC, DMX offers more flexible and precise controls. A single DMX controller can control up to 512 channels per universe (a group of DMX fixtures). This allows you to remotely control the power, brightness, and color of specific LEDs. DMX is suitable for large-scale installations like stage lighting, architectural lighting, etc.
DALI Control
For more advanced and flexible control of LEDs, DALI is an excellent alternative to TRIAC. It works best with DALI lighting, LED downlights, LED accent lights, and LED linear systems. To wire DALI dimming, you need a control cable with two cores. After the initial installation is done, the lighting management systems make it possible to rewire the lighting circuits digitally.
They offer a wide range of dimming capabilities that no modern dimming technology can beat. Because of this, you can use the most recent version of DALI to control both RGBW and tunable white lighting. Besides, dimming blasters with DALI standards can easily handle even the most complicated color-changing applications.
DALI and DMX are similar systems, but DALI has a bit more complex controlling system. Besides, they can perform automatic addressing, but DMX can’t.
FAQs
Your TRIAC dimmer may face flicker issues due to the fixture being incompatible. Besides, loose wiring and overloading dimmer capacity can also cause flickering.
TRIAC dimmers minimize the power delivery to the LEDs and, thus, can save energy. However, compared to other dimming options like PWM, TRIAC is less energy efficient.
Yes, installing a TRIAC dimmer is easy, and you can install it yourself without any external wiring. This can be set up into your existing power outlet. All you need to do is remove the existing switchboard and fit the TRIAC dimmer in it.
TRIAC dimming is forward phase-cut dimming. It is the most common type of dimming. This is also known as “incandescent dimming” or “Triac dimming.”
The term TRIAC transformer is not a standardized name. This refers to the transformer that uses a TRIAC technology to manage AC electricity. By this, you can understand a setup where TRIAC controls voltage or current flow for effective power regulation.
Traditional TRIAC dimming is a leading-edge dimmer. These are usually used in incandescent, halogen, LEDs, and other fixtures that have high power consumption. However, trailing-edge TRIAC dimmers are also available. These are specialized dimmers designed for applications that deal with low power consumption. As most LEDs run at low voltage and consume minimal energy, trial edge TRIAC dimmers are best for LED lighting.
Yes, TRIAC dimmers are compatible with 230V. It supports main voltage ranging from 100V to 240V. This is what makes them ideal for residential and commercial lighting applications.
Dimmers can be of different types based on technology. For instance- TRIAC, PWM, 0-10V, 1-10V, DALI, and DMX dimmer.
LEDs are sensitive to voltage. Though you can dim the LED, reducing the voltage will bring inconsistent brightness and damage the LEDs. Thus, reducing the voltage to the actual requirement can reduce the LED lifespan. Most importantly, the brightness of the LED mostly depends on current flow rather than voltage. However, excess current will overheat the chip and damage it.
The TRIAC dimmers don’t necessarily need neutral wire; they work fine with live and load wire. However, depending on the design and configuration of the dimmer switch, you may need neutral wire in some cases. For example, using single-pole switches to control TRIAC dimmers needs neutral wiring.
The TRIAC dimmable LED driver checks the input phase or RMS voltage when turned on. This determines the dimming current. Most TRIAC-dimmable LED drivers have “bleeding” circuits. Bleeding circuits keep the TRIAC active. This usually requires replacing the bleeding circuit. Adding power and control circuitry changes it.
First, connect the L/N terminals of the LED drivers to the OUTPUT on the dimmer. In the second step, connect the positive (LED+) and negative (LED-) ends of the LED driver to the input port of the light. In the final step, connect the input of the dimmer to a power source.
Electronic Low Voltage, or ELV, is the power produced by electronic devices. Electronic dimmer switches are known by several names, such as low-voltage electronic dimmers and trailing edge dimmers. This dimmer gradually brightens and dims your LED.
MLV dimmers are also called Magnetic Low Voltage (MLV) transformers. These are used to control magnetic low-voltage transformers in low-voltage lighting fixtures. You can use these transformers in low-voltage lighting fixtures.
ELV dimmers and transformers are usually more expensive than MLV transformers. However, ELV works more quietly, provides better control, and usually lasts longer than MLV.
0-10V dimming refers to a standard analog dimmer control. This method is also known as dimming through a 0-10V signal. It is different from the Triac dimming method in that it adds two ports on the driver for +10V and -10V. By changing the voltage from 1 to 10V, it is possible to control the amount of current that the driver sends and create a dimming effect.
The TRIAC trigger circuit lets the dimmer charge up before turning it back on. These seemingly random restarts of several TRIACs cause noise and LEDs to flicker.
Wrapping UP
When purchasing a TRIAC dimming for your LED fixture, make sure it is compatible with the other. You should also consider the voltage of the light as TRIAC operates on standard AC voltage. Therefore, to control low-voltage LED lights like LED strips that support DC, you must look for a TRIAC dimmer LED driver. You can check out our LEDYi TRIAC / Phase-Cut Dimmable LED Driver, which offers continuous, smooth, and stable light output. It supports a full Dimming range of 0-100% and comes with a 5-year warranty facility. So, order ASAP!