LED strips are more and more popular and are an excellent choice for commercial, residential, and industrial lighting. They are efficient, easy to install and require very little maintenance. You can customize LED strips in various shapes and sizes, so you can use them to light almost any space.
The main components of LED strips are SMD LEDs, FPCB(Flexible Printed Circuit Boards), resistors or other components. LED strips are manufactured by using a process called Surface Mount Technology (SMT) Assembly Process to mount LEDs, resistors and other components onto the FPCB.
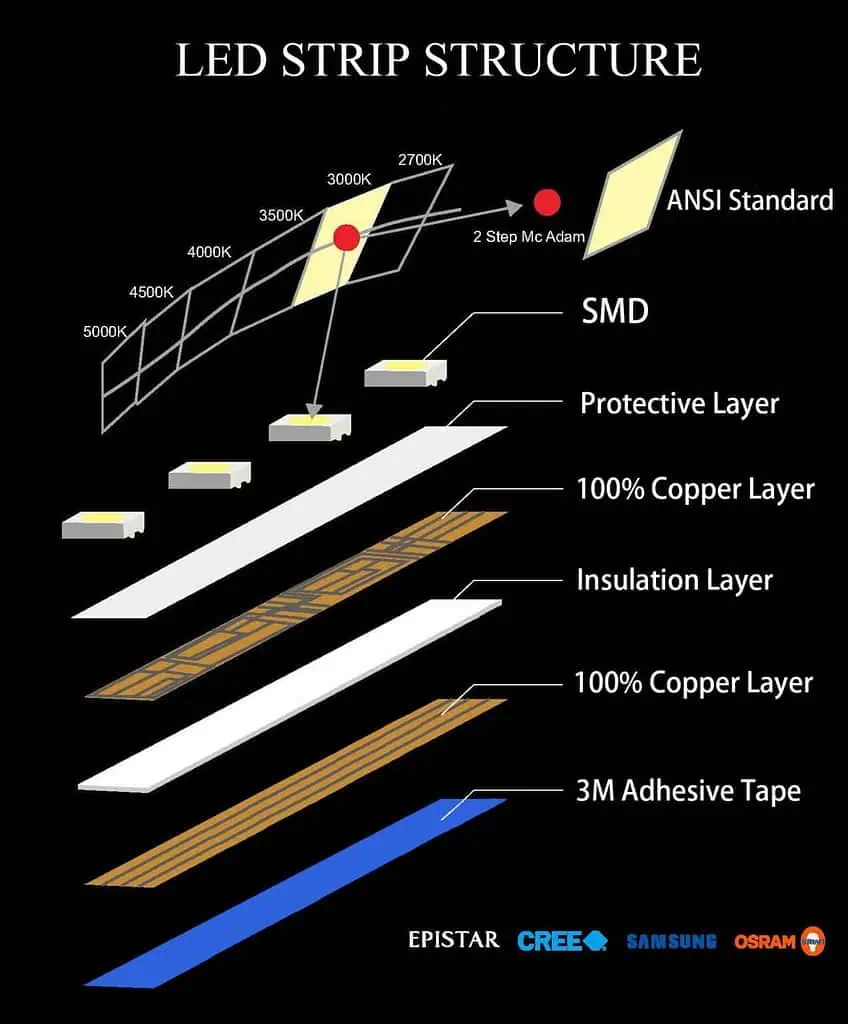
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor light source that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light (corresponding to the energy of the photons) is determined by the energy required for electrons to cross the band gap of the semiconductor. White light is obtained by using multiple semiconductors or a layer of light-emitting phosphor on the semiconductor device.
Most of the power consumed by LED strips comes from the power consumed by SMD LEDs.
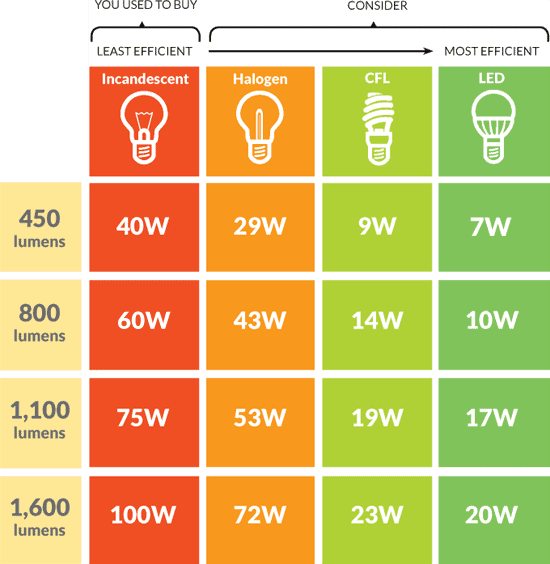
LEDs use less electricity and do not get particularly hot. They are illuminated entirely by the movement of electrons in a semiconductor material, and they have a lifespan as long as a standard transistor greater than 50,000 hours. LEDs have several advantages over conventional incandescent lamps, but their main advantage is efficiency. In incandescent lamps, the process of light production involves generating a lot of heat (the filament must be heated to be illuminated). Unless you use the incandescent lamp as a heater, this energy is completely wasted, as a large proportion of the available electricity is not used to produce visible light. Relatively speaking, LEDs produce very little heat. A higher percentage of the electrical energy is used directly to produce light, which significantly reduces the electrical demand.
LEDs output more lumens (or the amount of visible light) per watt than ordinary incandescent lamps. Light-emitting diodes have higher luminous efficiency (the efficiency with which electricity is converted to visible light) than incandescent lamps. A 60-watt incandescent lamp can produce 750-900 lumens, but you can get the same output from an LED bulb that uses only 6-8 watts.
How do I calculate the power consumption of an LED strip?
Before you can calculate the power consumption of an LED strip, you need to know the power per meter of the LED strip and how many meters of LED strip there are.
Common LED strips are available in 2.4W/m (0.73W/foot), 4.8W/m (1.46W/foot), 7.2W/m (2.19W/foot), 9.6W/m (2.93W/foot), 14.4W/m (4.39W/foot), 19.2W/m (5.85W/foot), 24W/m (7.32W/foot) etc.
For example, if there is a 5m LED strip with a power of 14.4W/m (1.46W/foot) and it works 12 hours a day, 365 days a year, how much electricity is used in a year?
The calculation is 14.4*5*12*365=315.360 KW.h
Conclusion
LED strips are very efficient and use less electricity than incandescent, halogen, and fluorescent lamps.
LEDYi manufactures high-quality LED strips and LED neon flex. All of our products go through high-tech laboratories to ensure the utmost quality. Besides, we offer customizable options on our LED strips and neon flex. So, for premium LED strip and LED neon flex, contact LEDYi ASAP!





