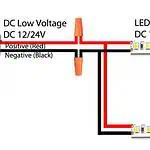
Have you ever wondered why your LED lights are flickering? Or why they aren’t as bright as they used to be? You may have noticed they’re getting unusually hot or not lasting as long as they should. These issues can often be traced back to the LED driver, a crucial component that regulates the power supplied to the light-emitting diode (LED). Understanding how to troubleshoot these issues can save you time, money, and frustration.
This comprehensive guide delves into the world of LED drivers, exploring common problems and their solutions. We’ll also provide resources for further reading, so you can deepen your understanding and become a pro at maintaining your LED lights.
Part 1: Understanding LED Drivers
LED drivers are the heart of LED lighting systems. They convert high-voltage, alternating current (AC) into low-voltage, direct current (DC) to power LEDs. Without them, LEDs would quickly burn out from the high voltage input. But what happens when the LED driver itself starts having issues? Let’s dive into the most common problems and their solutions.
Part 2: Common LED Driver Problems
2.1: Flickering or Flashing Lights
Flickering or flashing lights can indicate a problem with the LED driver. This can occur if the driver is not supplying a constant current, causing the LED to fluctuate in brightness. This is not only annoying but can also reduce the lifespan of the LED.
2.2: Inconsistent Brightness
Inconsistent brightness is another common issue. This can occur if the LED driver needs to supply the correct voltage. If the voltage is too high, the LED may be overly bright and burn out quickly. If it’s too low, the LED may be dimmer than expected.
2.3: Short Lifespan of LED Lights
LED lights are known for their long lifespan, but the driver could blame them if they burn out quickly. Overdriving the LEDs, or supplying them with too much current, can cause them to burn out prematurely.
2.4: Overheating Issues
Overheating is a common issue with LED drivers. This can occur if the driver needs to be adequately cooled or operating in a high-temperature environment. Overheating can cause the driver to fail and may also damage the LEDs.
2.5: LED Lights Not Turning On
The driver could be the issue if your LED lights aren’t turning on. This could be due to a failure in the driver itself or a problem with the power supply.
2.6: LED Lights Turning Off Unexpectedly
LED lights that turn off unexpectedly could be experiencing a problem with the driver. This could be due to overheating, a power supply issue, or a problem with the driver’s internal components.
2.7: LED Lights Not Dimming Properly
The driver could be to blame if your LED lights aren’t dimming properly. Not all drivers are compatible with all dimmers, so it’s important to check your driver’s and dimmer’s compatibility.
2.8: LED Driver Power Issues
Power issues can occur if the LED driver is not supplying the correct voltage or current. This can cause various issues, from flickering lights to LEDs that won’t turn on at all.
2.9: LED Driver Compatibility Issues
Compatibility issues can occur if the LED driver is incompatible with the LED or the power supply. This can cause various issues, including flickering lights, inconsistent brightness, and LEDs not turning on.
2.10: LED Driver Noise Issues
Noise issues can occur with LED drivers, particularly those using magnetic transformers. This can result in a humming or buzzing noise. While this doesn’t necessarily indicate a problem with the driver’s functionality, it can be annoying.
Part 3: Troubleshooting LED Driver Problems
Now that we’ve identified the common issues, let’s investigate how to troubleshoot them. Remember, safety comes first! Always turn off and unplug your LED lights before attempting any troubleshooting.
3.1: Troubleshooting Flickering or Flashing Lights
Step 1: Identify the problem. If your LED lights are flickering or flashing, this could indicate an issue with the LED driver.
Step 2: Check the driver’s input voltage. Use a voltmeter to measure the input voltage to the driver. If the voltage is too low, the driver may be unable to supply a constant current, causing the lights to flicker.
Step 3: If the input voltage is within the driver’s specified range, but the problem persists, the issue might be with the driver itself.
Step 4: Consider replacing the driver with a new one that matches the specifications of your LED lights. Make sure to disconnect the power before replacing the driver.
Step 5: After replacing the driver, test your LED lights again. If the flickering or flashing stops, the issue is likely with the old driver.
3.2: Troubleshooting Inconsistent Brightness
Step 1: Identify the problem. If your LED lights are not consistently bright, this could be due to an issue with the LED driver.
Step 2: Check the driver’s output voltage. Use a voltmeter to measure the output voltage from the driver. If the voltage is too high or too low, this could be causing inconsistent brightness.
Step 3: The driver might be the issue if your LEDs’ output voltage is not within the specified range.
Step 4: Consider replacing the driver with one that matches the voltage requirements of your LED lights. Remember to disconnect the power before replacing the driver.
Step 5: After replacing the driver, test your LED lights again. The issue was likely with the old driver if the brightness is now consistent.
3.3: Troubleshooting Short Lifespan of LED Lights
Step 1: Identify the problem. If your LED lights are burning out quickly, this could be due to an issue with the LED driver.
Step 2: Check the driver’s output current. Use an ammeter to measure the output current from the driver. If the current is too high, this could cause the LEDs to burn out prematurely.
Step 3: The driver might be the issue if your LEDs’ output current is not within the specified range.
Step 4: Consider replacing the driver with one that matches the current requirements of your LED lights. Remember to disconnect the power before replacing the driver.
Step 5: After replacing the driver, test your LED lights again. If they no longer burn out quickly, the issue was likely with the old driver.
3.4: Troubleshooting Overheating Issues
Step 1: Identify the problem. If your LED driver is overheating, this could be causing your LED lights to malfunction.
Step 2: Check the driver’s operating environment. If the driver is in a high-temperature environment or lacks proper ventilation, this could cause it to overheat.
Step 3: If the operating environment is within acceptable conditions, but the driver is still overheating, the issue might be with the driver.
Step 4: Consider replacing the driver with a higher temperature rating. Remember to disconnect the power before replacing the driver.
Step 5: After replacing the driver, test your LED lights again. If the driver no longer overheats, the issue was likely with the old driver.
3.5: Troubleshooting LED Lights Not Turning On
Step 1: Identify the problem. If your LED lights aren’t turning on, this could be an issue with the LED driver.
Step 2: Check the power supply. Ensure that the power supply is connected correctly and supplying the correct voltage. Use a voltmeter to measure the input voltage to the driver.
Step 3: If the power supply is functioning correctly, but the lights still don’t turn on, the driver might be the issue.
Step 4: Check the driver’s output voltage. Use a voltmeter to measure the output voltage from the driver. If the voltage is too low, this could be preventing the LEDs from turning on.
Step 5: If the output voltage is not within the specified range for your LEDs, consider replacing the driver with one that matches the voltage requirements of your LED lights. Remember to disconnect the power before replacing the driver.
Step 6: After replacing the driver, test your LED lights again. If they now turn on, then the issue was likely with the old driver.
3.6: Troubleshooting LED Lights Turning Off Unexpectedly
Step 1: Identify the problem. If your LED lights turn off unexpectedly, this could be an issue with the LED driver.
Step 2: Check for overheating. If the driver is overheating, it may shut down to prevent damage. Ensure the driver is adequately cooled and not operating in a high-temperature environment.
Step 3: If the driver is not overheating, but the lights still turn off unexpectedly, the issue might be with the power supply.
Step 4: Check the power supply. Use a voltmeter to measure the input voltage to the driver. If the voltage is too low or too high, this could cause the lights to turn off.
Step 5: Consider replacing the driver if the power supply functions correctly but the lights still turn off. Remember to disconnect the power before replacing the driver.
Step 6: After replacing the driver, test your LED lights again. If they no longer turn off unexpectedly, the issue was likely with the old driver.
3.7: Troubleshooting LED Lights Not Dimming Properly
Step 1: Identify the problem. If your LED lights aren’t dimming correctly, this could be due to an issue with the LED driver.
Step 2: Check the compatibility of your driver and dimmer. Not all drivers are compatible with all dimmers, so ensure they match.
Step 3: If the driver and dimmer are compatible, but the lights still don’t dim properly, the driver might be the issue.
Step 4: Consider replacing the driver with one designed for dimming. Remember to disconnect the power before replacing the driver.
Step 5: After replacing the driver, test your LED lights again. If they now dim correctly, the issue was likely with the old driver.
3.8: Troubleshooting LED Driver Power Issues
Step 1: Identify the problem. If your LED lights are experiencing power issues, such as flickering or not turning on, this could be due to an issue with the LED driver.
Step 2: Check the driver’s input voltage. Use a voltmeter to measure the input voltage to the driver. If the voltage is too low or too high, this could be causing the power.
Step 3: If the input voltage is within the specified range, but the power issues persist, the driver might be the issue.
Step 4: Check the driver’s output voltage. Use a voltmeter to measure the output voltage from the driver. If the voltage is too low or too high, this could be causing the power.
Step 5: If the output voltage is not within the specified range for your LEDs, consider replacing the driver with one that matches the voltage requirements of your LED lights. Remember to disconnect the power before replacing the driver.
Step 6: After replacing the driver, test your LED lights again. If the power issues are resolved, the problem is likely with the old driver.
3.9: Troubleshooting LED Driver Compatibility Issues
Step 1: Identify the problem. If your LED lights are experiencing compatibility issues, such as flickering or not turning on, this could be due to an issue with the LED driver.
Step 2: Check the compatibility of your driver, LEDs, and power supply. Ensure that all components are compatible with each other.
Step 3: If all components are compatible, but the issues persist, the driver might be the issue.
Step 4: Consider replacing the driver with one compatible with your LEDs and power supply. Remember to disconnect the power before replacing the driver.
Step 5: After replacing the driver, test your LED lights again. If the compatibility issues are resolved, the problem is likely with the old driver.
3.10: Troubleshooting LED Driver Noise Issues
Step 1: Identify the problem. If your LED driver is making a humming or buzzing noise, this could be due to the type of transformer it uses.
Step 2: Check the type of transformer in your driver. Drivers that use magnetic transformers can sometimes make noise.
Step 3: If your driver uses a magnetic transformer and is making noise, consider replacing it with a driver that uses an electronic transformer, which tends to be quieter.
Step 4: After replacing the driver, test your LED lights again. If the noise is gone, the issue was likely with the old driver.
Part 4: Preventing LED Driver Issues
Preventing LED driver issues is often a matter of regular maintenance and checks. Ensure your driver is adequately cooled and not operating in a high-temperature environment. Regularly check the input and output voltage and current to ensure they’re within the specified ranges. Also, ensure your driver, LEDs, and power supply are compatible.
FAQs
An LED driver is a device that regulates the power supplied to an LED light. It’s important because it converts high-voltage, alternating current (AC) into low-voltage, direct current (DC), which is necessary to operate LED lights.
This could be a sign of a problem with the LED driver. If the driver is not supplying a constant current, it can cause the LED to fluctuate in brightness, resulting in flickering or flashing lights.
This could be due to an issue with the LED driver not supplying the correct voltage. If the voltage is too high, the LED may be overly bright and burn out quickly. If it’s too low, the LED may be dimmer than expected.
If your LED lights burn out quickly, the LED driver could be to blame. Overdriving the LEDs, or supplying them with too much current, can cause them to burn out prematurely.
Overheating can occur if the LED driver needs to be properly cooled or operating in a high-temperature environment. Overheating can cause the driver to fail and may also damage the LEDs.
The driver could be the issue if your LED lights aren’t turning on. This could be due to a failure in the driver itself or a problem with the power supply.
LED lights that turn off unexpectedly could be experiencing a problem with the driver. This could be due to overheating, a power supply issue, or a problem with the driver’s internal components.
The driver could be to blame if your LED lights aren’t dimming correctly. Not all drivers are compatible with all dimmers, so it’s important to check your driver’s and dimmer’s compatibility.
Power issues can occur if the LED driver is not supplying the correct voltage or current. This can cause various issues, from flickering lights to LEDs that won’t turn on at all.
Noise issues can occur with LED drivers, particularly those using magnetic transformers. This can result in a humming or buzzing noise. While this doesn’t necessarily indicate a problem with the driver’s functionality, it can be annoying.
Conclusion
Understanding and troubleshooting LED driver issues is crucial for maintaining your LED lights. By identifying common problems and their solutions, you can save time, money, and frustration. Prevention is often the best cure, so regular maintenance and checks are critical. We hope this guide has been helpful and encourages you to apply the knowledge gained to maintain your LED lights.